From our experience, we know that there are a lot of SEO questions from merchants concerning the structure of their online store, effective URLs, Titles, H1 and so on.
And the situation is that even the most professional developer for Magento ® cannot answer such questions correctly. Why? Because only certain online store clients know the real truth. In this article, we’d like to provide the algorithm of the semantic UI kernel development which can help us address the most problematic SEO issues and give us more hints how to make Magento ® online store more profitable.
Semantic UI Kernel Defined
It is the structured database of search keywords, phrases and their morphological forms, which most accurately characterize the products or services offered by an online store, and have been specially selected for its promotion.
If the semantic UI kernel for your Magento ® store was developed correctly and carefully, it is able to:
- Increase organic traffic
- Reduce context Ads cost
- Increase conversion
Some product pages do not exist for users because the user can’t find this page using search engines.
Can you imagine a woman searching for a satchel bag using its serial number 38226?
And not all clients use the usual requests like “black lady bag”. In fact, very often it is possible to find the necessary product page only using the filters by product attributes. Our company provides a special Navigation extension for Magento ® which allows setting filters in Magento ® online stores.
But it is not enough to implement only a technical solution. The main problem is that all attributes and search criteria must be identified. There are a large number of words that can be used to express what a certain persons needs and and that is why a lot of search criteria can be found.
In the online store semantic UI kernel development, the main task is to collect all possible requests. Let’s review an algorithm for this procedure.
1. Find all basic or top-level requests. These requests can be determined as product groups in the category. For example, “men’s shoes” is a good top-level request. The basic requests can be identical to the site menu.
2. Using the basic request find all possible requests that people can use to find the products.
The most popular keyword planner tool is Google AdWords which allows searching keyword ideas. All requests can be as:
- High-frequency is greater than 2000 / month
- Midrange to 2,000 / month
- Low-frequency less than 700 / month
The division is like a proposition, and it strongly depends on the industry. Usually, the high-frequency requests have more competition and the promotion is more complex as a result.
There are some recommendations on this step:
- In this procedure, it is important to remove inappropriate word combinations from the requests list. For example, “women bags” can also include the request such as “handmade bags”, and if such products category is not provided, it should be eliminated. Only the target requests should be collected.
- Don’t forget to delete all “stop words”. The words such as: ‘and’, ‘or’, ‘about’, ‘of’, ‘the’, etc. are not very good for SEO, because they use character space and may interfere to convey the meaning for search robots.
- The words order in the request may be important and we recommend paying attention to this. For example, “PVC windows & doors” can be identical to “PVC doors & windows”. But “Paris to New York Flights” is not identical to “New York to Paris Flights” and there are two different customers’ needs.
- The competitors’ requests are also very important. You can use different services to identify them. We can recommend paying attention to semrush.com and ahrefs.com. They can give competitive analytics not only concerning keywords but a lot of other useful information too.
3. Clean the lists of requests carefully. All untargeted requests misspelled requests, very long requests, requests for multiple interpretations, requests relating to other regions, irrelevant requests must be eliminated from the list. To understand this task better, here are some examples.
For the website of a real estate agency which offers premium property in the USA, a request such as “real estate in the USA” can be useless because it is very common and, if people really need a property, they make their query detailed. So, such requests can generate useless traffic and it is not good for your website. But “elite real estate”, “luxury properties” and “premium property” can be more productive.
For the music online store the request “free mp3 download” is untargeted because this audience is not going to spend money and there will be users who leave the store very quickly and this fact will increase the online store bounce rate.
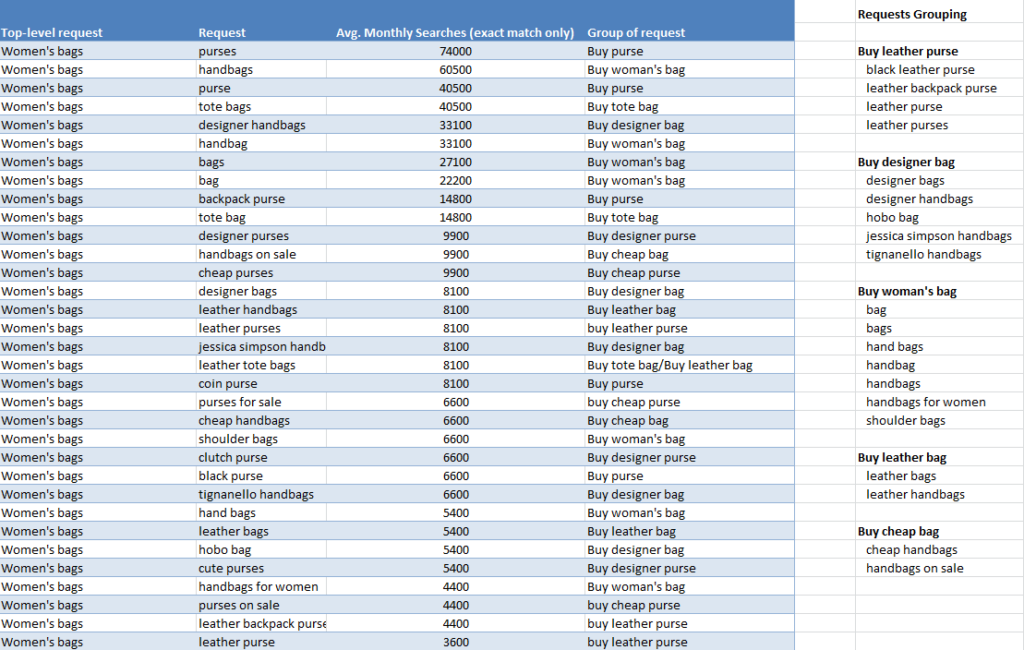
4. Group the requests and distribute requests groups by categories. Each group of requests must solve a specific client’s problem. It’s up to you how specific these groups should be. Here is an example of how to distribute requests by groups.
It is significant to identify all groups carefully because, based on these results, the categories and product attributes will be determined.
This is an important question! Is it a category or a product attribute? To promote and optimize the product or certain group of products for Google you need to have a separate landing page and so you need to create a category. In other cases, all product characteristics can be as the attributes which users can use in Navigation to filter and select what they need.
The request can be considered as the client’s problem that must be solved or at client’s request. Such problems and needs may be more than a product. Therefore, specific categories can be created for special customer needs, and the particular product page can be presented in several categories. In this case, the same product page can have different URLs, and there is a problem with duplicate content. To solve it, we recommend checking out our SEO extension for Magento ®.
5. Create or modify web store structure. Add new categories. Attach the attributes to the products and categories. On this step, the new pages as the categories and new attributes will be added. To implement new pages in the current site structure is a more complicated task than to develop a structure for a new online store. Some requests can be on the Google TOP – 10 results and certain pages can have SEO optimized text which generates good traffic and it is better not to make any changes. Some new pages can start to compete with old pages which are on the top of Google. The task is really complex and the main rule in this step is “Don’t break something that already works”.
6. Content. URL, Title, H1, H2, description.
Now there is all necessary information to assign to copywriters. It is clear what keywords and word combinations should be in the text for each page.
Here are some recommendations to the page headers:
- URL = the most popular and promoted group request
- Title = the most popular and promoted group request
- H1 = the most popular request in the group (should be paraphrasing)
- H2 = the popular group request
In conclusion, it is necessary to pay attention that after successful implementation the semantic UI kernel can be expanded. It is better to do this in a few months after promotion campaign when the website has reached the necessary Google positions.